 US-based BWX Technologies (BWXT) announced that its TRISO nuclear fuel manufacturing restart activities are continuing to progress ahead of schedule.
US-based BWX Technologies (BWXT) announced that its TRISO nuclear fuel manufacturing restart activities are continuing to progress ahead of schedule.
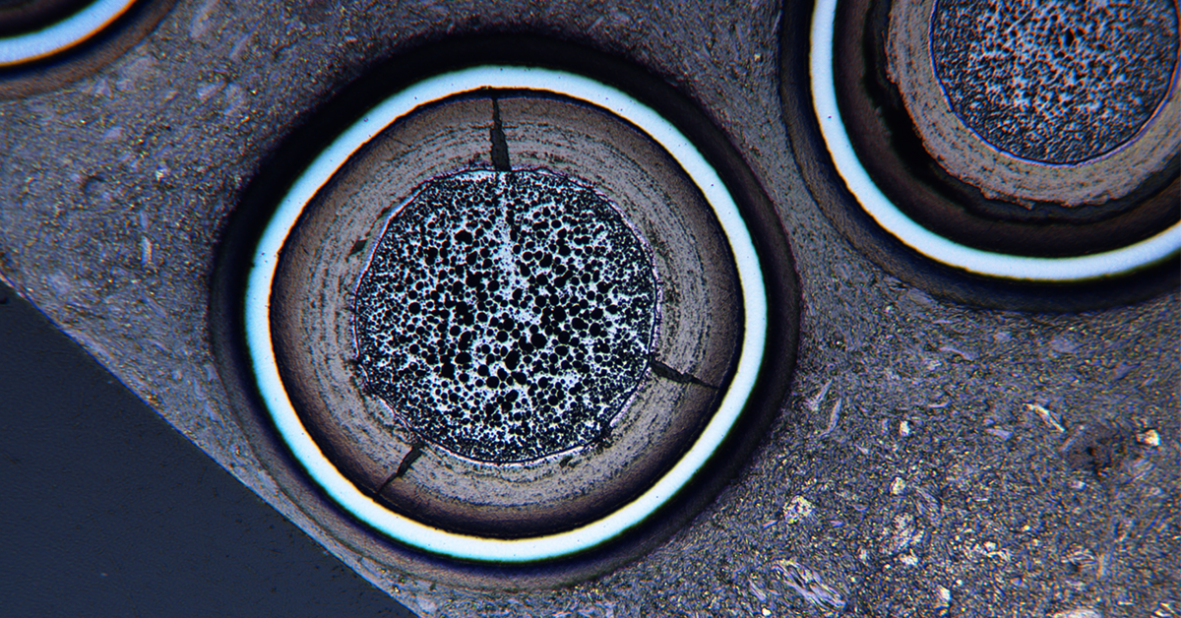
BWXT has demonstrated the capability to form and sinter uranium oxycarbide (UCO) fuel kernels that serve as a precursor to the TRISO coating process. Sintering is a process by which heat and pressure are applied to form a solid fuel kernel, BWXT said.
With the completion of these activities, BWXT is now focusing on bringing an additional sintering furnace and a coating furnace online to meet projected production demand.
Last year, BWXT produced uranium solutions for TRISO fuel as the company progressed with its plans to restart its manufacturing line and increase capacity at its facility in Lynchburg, Virginia.
BWXT is restarting its TRISO fuel production capability and increasing its capacity to position the company to meet new client interests in the US Department of Defense microreactors, space reactors, and advanced civil reactors.
“BWXT has been working expeditiously to complete our preparations to restart our TRISO line and produce TRISO fuel at scale,” said Joel Duling, president of BWXT Nuclear Operations Group, Inc. “I can’t say enough about how well our employees have performed to get us to this stage and position us to finish our restart efforts later this year, even in the face of recent challenges across the globe. The effort and accomplishment is truly phenomenal.”
TRISO is a shortened form of the term TRIstructural-ISOtropic. TRIstructural refers to the layers of coatings surrounding the uranium fuel kernel. ISOtropic refers to the coatings having uniform materials characteristics in all directions so that fission products are essentially retained.
TRISO fuel can withstand extreme heat and has very low proliferation concerns and environmental risks, BWXT said.
Photo: TRISO fuel (Credit: Department of Energy)






